- Platform
- Solutions
- Expose and Manage ThreatsContinuously identify, expose and remediate critical threats
- Reduce Attack SurfaceThe roadmap to reducing your attack surface
- Control Subsidiary RiskManage cyber risk across all your subsidiaries
- Cloud Attack SurfaceClose Security Gaps Across Your Cloud Attack Surface
- Improve Security PostureReduce risk systematically
- Manage M&A riskEvaluate candidate’s cyber risk
- Learn
- Company
Threat Exposure Radar ExplainedSolutions
Ionix Connective IntelligenceProductA
Acceptable Risk
Understanding acceptable risk requires a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s risk appetite, regulatory requirements, and business objectives. While some risks may be deemed acceptable due to their low likelihood or potential impact, others may require immediate mitigation strategies to align with organizational goals and compliance standards. Moreover, acceptable risk varies across different industries and sectors,...Access Control (or Access Management)
Effective access control is fundamental to maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of organizational data and resources, mitigating the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. By implementing access control measures, organizations can enforce security policies and restrictions tailored to individual user roles, responsibilities, and privileges, ensuring that users only access information and...Active Asset
Active assets play a critical role in an organization’s attack surface, representing components that are actively utilized in day-to-day operations. Distinguishing between active and inactive assets is vital for effective attack surface reduction, as it enables organizations to prioritize the removal or consolidation of redundant or unnecessary assets without disrupting critical business processes. By accurately...Application Programming Interface (API)
An application programming interface (API) is a set of rules and protocols that enable two applications to communicate with each other and share data. Application developers use APIs to integrate the functions of one application into another without coding those capabilities from scratch. Nearly every application makes use of at least one API today. However,...Asset
In the context of attack surface management, an asset is an IT element such as an application, code, website, server, or another element that provides a point of entry for a cyber attacker to breach a network, system, application, or device. The external attack surface comprises all internet-facing IT assets, both known and unknown. Assets...Asset Discovery
Asset discovery serves as a foundational pillar of effective cybersecurity strategy, providing organizations with comprehensive visibility into the intricate web of IT assets comprising their attack surface. This multifaceted process encompasses the identification and categorization of various asset types, ranging from traditional on-premises systems and network infrastructure to cloud-based services, IoT devices, and endpoints dispersed...At-Risk Asset (or Asset Risk)
Conducting a risk assessment for internet-facing IT assets is essential for organizations to effectively prioritize their cybersecurity efforts and allocate resources based on the level of risk posed by each asset. By considering contextual factors such as usage patterns, ownership, connectivity, and vulnerability status, organizations can gain insights into the potential impact of security incidents...Attack Surface Assessment
Conducting an attack surface assessment is essential for organizations to gain insights into their security posture and identify potential weaknesses that could be exploited by threat actors. By adopting an attacker’s perspective, organizations can proactively identify and prioritize security measures to mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of successful cyber attacks. During the assessment, factors...Attack Surface Element
Attack surface elements constitute the diverse array of internet-facing assets within an organization’s digital infrastructure that are susceptible to exploitation by cyber threats and adversaries. These elements encompass a wide range of components, including physical devices such as routers, switches, and IoT devices; networks and server infrastructure deployed on-premises or in the cloud; externally accessible...Attack Surface Inventory
Attack surface inventory is the complete accounting of all assets or elements that make up a company’s attack surface and can include both first-party assets and assets that the company does not directly own or control. It’s the result of an asset discovery process.Attack Surface Management
Effective attack surface management requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to evolving threats and technological landscapes. This involves not only discovering assets and identifying vulnerabilities but also implementing proactive measures to reduce the attack surface and mitigate potential risks. Furthermore, attack surface management encompasses strategic decision-making to prioritize remediation efforts based on risk severity and potential...Attack Surface Monitoring
In addition to continuously scanning the organization’s attack surface, effective attack surface monitoring involves analyzing the gathered data to gain insights into emerging threats and potential vulnerabilities. This includes correlating security events, identifying patterns indicative of malicious activity, and prioritizing remediation efforts based on risk severity. Moreover, attack surface monitoring integrates threat intelligence feeds and...Attack Surface Reduction
Implementing effective attack surface reduction measures requires a proactive and holistic approach to security management. Beyond identifying and patching vulnerabilities, organizations must also prioritize reducing the overall attack surface to minimize exposure to potential threats. This involves regularly assessing and optimizing the organization’s digital footprint, identifying and decommissioning outdated or unnecessary assets, and implementing stringent...Attack Surface Visibility
Achieving comprehensive attack surface visibility is essential for organizations to proactively manage security risks and effectively protect their assets from potential threats. By leveraging supply chain discovery and attack surface monitoring tools, organizations can gain insights into their digital footprint, including assets, dependencies, and potential attack vectors. This visibility enables organizations to conduct thorough inventory...Attack Vector
Attack vectors represent the diverse tactics and techniques employed by threat actors to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise the security of IT systems and networks. These vectors encompass a wide range of attack methods, including technical exploits, social engineering tactics, and malicious activities aimed at infiltrating, manipulating, or disrupting targeted systems and data. Common attack vectors...C
Classification
Classification plays a vital role in effective risk management and prioritization of cybersecurity efforts within an organization. By systematically categorizing assets and vulnerabilities according to their severity and potential impact on business operations, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently and focus on mitigating the most critical risks first. This approach helps organizations prioritize remediation efforts...Cloud Asset
Cloud assets encompass a diverse range of IT resources and components that are leveraged for cloud computing purposes within an organization’s digital infrastructure. These assets include virtual or physical servers, storage systems, databases, networking infrastructure, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that are hosted and managed within cloud environments, such as public, private, or hybrid clouds. Unlike...Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database serves as a critical resource for the cybersecurity community, facilitating the sharing of information about known vulnerabilities and exposures to enhance collective defense efforts against cyber threats. By providing a standardized naming scheme and unique identifier for each reported vulnerability, CVE enables organizations to quickly and accurately reference...Continuous Discovery
Continuous discovery is the process of constantly scanning the digital supply chain to identify previously unknown assets and vulnerabilities. It’s a necessary component of effective attack surface management.Credential Theft
Credential theft occurs when malicious actors steal login details and use them to access services or applications. Threat actors then steadily elevate their privileges or access bank accounts, e-commerce websites, and other platforms as a customer. Credential theft can cause significant financial losses for victims (both companies and the affected customers). When used in the...Cyber Risk
Managing cyber risk involves not only preventing data breaches but also implementing proactive measures to mitigate potential harm to the organization’s finances, intellectual property, and reputation. This includes assessing and prioritizing potential threats, implementing robust security controls and protocols, conducting regular security audits and assessments, and ensuring rapid response and recovery mechanisms in the event...Cyber Risk Assessment
A cyber risk assessment evaluates an asset, vulnerability, or system as a whole to determine the likelihood of a breach and the potential consequences of an exploit.Cyber Risk Quantification
Cyber risk quantification serves as a critical component of cybersecurity risk management, enabling organizations to assess and quantify the potential impact and severity of cyber threats and vulnerabilities on their business operations and assets. By applying quantitative analysis techniques and methodologies, organizations can measure the potential consequences of a data breach or security incident targeting...D
Data Breach
A data breach exposes sensitive data to unauthorized users. Basically, any data accessed by an unauthorized audience is a data breach. For enterprises, data breaches can result in lost intellectual property and consumer trust, as well as millions of dollars in fines, depending on the severity.Decommissioning
Decommissioning is the process of removing an asset from a company’s network and properly disposing of it or recycling it while ensuring that no information can be retrieved from it. It’s a common practice when upgrading hardware components such as servers, laptops, and entire data centers. Failure to decommission an asset properly means it remains...Defense in Depth
Defense in depth, synonymous with layered security, is a fundamental principle in cybersecurity aimed at establishing multiple lines of defense to protect against a wide range of cyber threats and attacks. By deploying diverse security controls across different layers of an organization’s IT infrastructure, defense in depth seeks to create a comprehensive security posture that...Digital Supply Chain
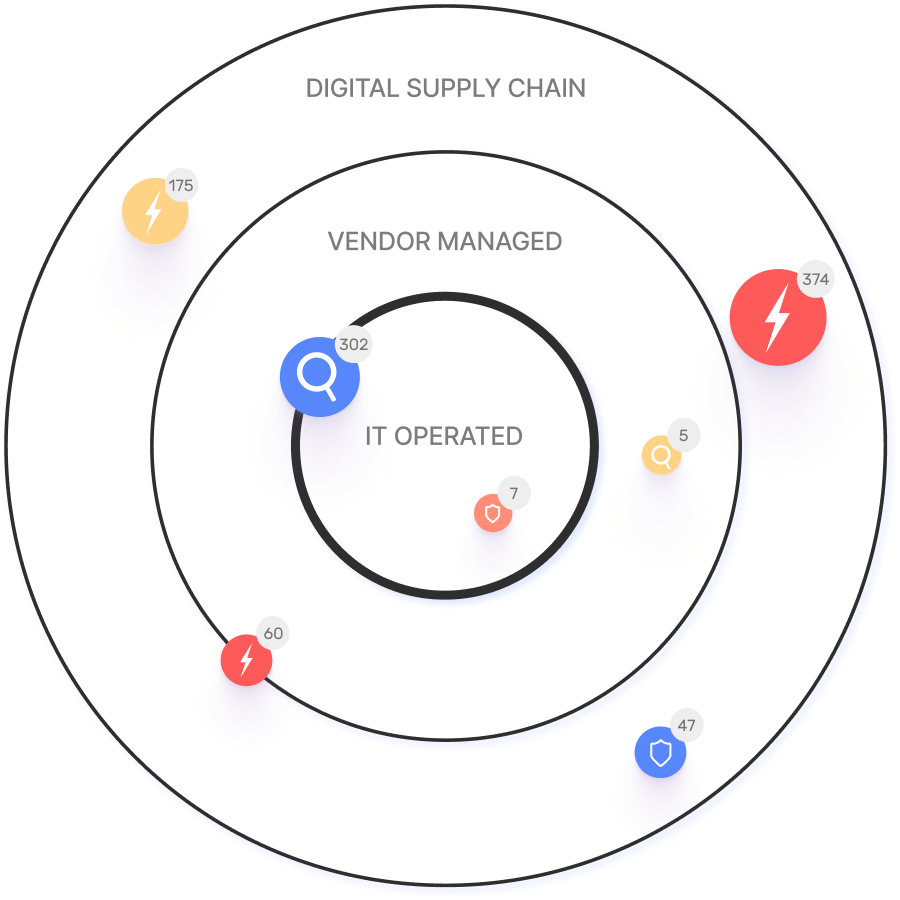
The Digital Supply Chain represents a fundamental shift in how businesses procure, produce, and distribute goods and services, driven by the widespread adoption of internet-based technologies and digital transformation initiatives. Traditionally, supply chains were characterized by physical goods and linear processes, but the advent of web-based services and applications has transformed these traditional models into...E
Encryption
Encryption stands as a fundamental security mechanism utilized to protect sensitive information and communications from unauthorized access and interception. By employing cryptographic algorithms, encryption transforms plaintext data into ciphertext, rendering it indecipherable to anyone without the appropriate decryption key. This process ensures data confidentiality and integrity, safeguarding it from eavesdropping, tampering, and unauthorized disclosure while...Exploit (or Exploitation)
An exploit is a code, command sequence, or program that takes advantage of a security flaw or vulnerability to gain access to an application or network. Hackers use exploits to steal data, install malware, or cause other unintended behavior.Exposure
An exposure is a misconfiguration or a flaw in a software application that enables threat actors to gain unauthorized access to an application or network.F
False Positive
False positives pose significant challenges for IT security teams, requiring careful attention and resources to distinguish between legitimate threats and erroneous alerts. While false positives are an inevitable aspect of security monitoring systems, their prevalence can overwhelm security teams, diverting valuable time and resources away from addressing genuine security threats. Moreover, the sheer volume of...Fourth Parties
Your enterprise is aware of the risks it assumes when working with a third-party vendor. But what about the vendors used by those third parties? They have their own digital supply chain of vendors, IT infrastructures, dependencies, and resources. And each element in these supply chains exposes you to more and more potential risk. Multiply...I
Inactive Asset
In the realm of attack surface management, an inactive asset represents a dormant yet latent vulnerability within an organization’s digital ecosystem. These internet-facing IT elements, while not actively utilized in current operations, remain interconnected with first-party, active assets, thereby extending the organization’s attack surface and potentially exposing it to cyber threats and malicious actors. Despite...Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations seeking to leverage the benefits of interconnected technologies while mitigating associated security risks. IoT devices, ranging from smart thermostats and wearable devices to industrial sensors and medical devices, introduce new entry points and attack vectors into organizational networks, expanding the attack surface and...K
Known Asset
Known assets represent the identifiable components within an organization’s IT infrastructure that are recognized and acknowledged by the company’s IT management or security teams. These assets encompass a broad spectrum of digital resources, including hardware devices, software applications, network infrastructure, databases, and cloud services, among others, that are integral to the organization’s business operations and...L
Layered Security
Layered security is a cybersecurity approach that implements multiple layers of security controls. If an attacker manages to get past one security control, they have one or more additional security measures to evade if they’re targeting a system with layered security. Think of the additional security layers as fail-safes or backup measures. Layered security is...Legacy IT
Legacy IT environments present significant challenges for organizations due to their outdated and often unsupported nature, increasing the risk of security vulnerabilities, system failures, and compatibility issues. Despite their critical role in supporting essential business functions, legacy systems may lack modern security features and updates, leaving them susceptible to exploitation by cybercriminals and malware attacks....M
Malicious Asset
A malicious asset, also known as a rogue asset, is created by a threat actor or unauthorized user to target a company. Phishing websites or mobile applications designed to appear as those owned by the target company, typo-squatted domains, and stolen data sets shared or sold on the dark web are examples of malicious assets.Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) represent strategic initiatives undertaken by organizations to expand their market presence, diversify their product portfolios, or achieve synergies through business consolidation. However, M&A transactions inherently introduce complexities and risks, including cybersecurity concerns related to the expanded attack surface and integration of disparate IT environments. The combination of multiple business entities and...Misconfiguration
Misconfiguration is when an application’s or system’s settings are not selected or improperly implemented, which can leave the application or system vulnerable to unauthorized access. Misconfiguration can occur in a network, application, cloud infrastructure, and any component with settings.Mitigation
In the context of cybersecurity, mitigation is a damage control process that does not completely eradicate a vulnerability or threat but minimizes the potential negative consequences that could occur with a breach.N
Network Penetration
Network penetration testing plays a crucial role in assessing an organization’s security posture and identifying weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, penetration testers can uncover vulnerabilities in network configurations, software systems, and user privileges, allowing organizations to prioritize remediation efforts and strengthen their defenses against cyber threats. Moreover,...Network Segmentation
Network segmentation creates barriers between different areas of a network, allowing each subnetwork to function independently. It’s a strategy that helps to reduce the attack surface. If a threat actor manages to access one network segment, they could not access other segments or spread malware automatically throughout the entire network.Nth Parties
Nth parties pose the same risk to your enterprise as third parties but are significantly more difficult to track: they are the vendors, services, applications, and IT infrastructures of your vendors’ vendors. That’s right: they are connected to your organization by “nth” degrees of separation within your cyber supply chain.O
Open Source Software (OSS)
While open source software offers numerous benefits, including transparency, flexibility, and community collaboration, organizations must also be aware of the associated security risks. The decentralized nature of open source development means that vulnerabilities may exist in widely used OSS components, leaving organizations vulnerable to supply chain attacks and exploitation by threat actors. To mitigate these...Orphaned Asset (or Orphaned App)
Orphaned assets are IT assets that lack identifiable origins or connections and are not readily visible to security teams as a result. Examples include virtual machines that have no physical host and applications that have been abandoned and have no clear administrator or manager. These assets are often left exposed, making them ideal targets for...P
Penetration Test
A penetration test is a type of security test that simulates a hacker breaking into a network or system to evaluate the strength of a company’s security controls.Principle of Least Functionality
By adhering to the principle of least functionality, organizations can minimize the attack surface and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access or exploitation. This approach helps reduce the potential impact of security breaches and limits the avenues available to attackers seeking to compromise the system. Additionally, implementing the principle of least functionality can enhance system...Principle of Least Privilege
The principle of least privilege is a strategy that limits the access and capabilities of a user to the minimum necessary to perform their job duties. If a threat actor tricks a user into revealing their credentials, they cannot access higher-level functionality or data than the victim’s privileges allow.Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of processes, hardware and software components, and other elements involved in managing digital certificates and public-key encryption. SSL certificates, for instance, are managed by PKI. These certificates assure website visitors that they’re sending information to the intended recipient. Several problems associated with PKI can create vulnerabilities, such as...R
Red Team
A red team comprises a group of IT professionals (either internal company employees or a third-party contractor) that simulates the potential actions of a threat actor to test a company’s cybersecurity posture. The individuals that compose a red team are also known as ethical hackers. Red teaming is the process of challenging every security control,...Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in information and cybersecurity constitutes a vital framework for protecting sensitive data, preserving consumer privacy, and mitigating the risk of cyber threats across various industries and sectors. Regulatory requirements are established by governmental bodies, industry regulators, and standards organizations to enforce specific rules and standards aimed at safeguarding critical information assets and ensuring...Remediation
Remediation represents the comprehensive process of addressing and resolving identified risks or threats within an organization’s cybersecurity landscape. It involves implementing corrective measures and controls to eliminate vulnerabilities, mitigate potential harm, and strengthen the overall security posture. Remediation efforts aim to eradicate the root cause of security weaknesses and prevent their exploitation by threat actors,...Reputational Risk
Beyond immediate financial impacts, reputational risk can have far-reaching consequences for an organization’s brand equity and market position. Mitigating reputational risk often requires multifaceted strategies, including prompt and transparent communication, swift resolution of issues, and proactive measures to prevent recurrence. Furthermore, investing in comprehensive security measures not only safeguards customer data but also fosters a...Risk Assessment
Conducting a comprehensive cybersecurity risk assessment is critical for organizations to identify, prioritize, and mitigate potential threats and vulnerabilities to their information assets and systems. Beyond regulatory compliance requirements, risk assessments serve as proactive measures to enhance cybersecurity posture and resilience against evolving cyber threats and attacks. By systematically evaluating the organization’s IT infrastructure, processes,...Risk Indicator
Risk indicators play a critical role in helping security teams assess and monitor the organization’s cybersecurity posture, identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, and prioritize remediation efforts to mitigate risks effectively. By tracking key risk indicators such as CVEs, certificate validity, unauthorized IT assets, and compliance status, security teams can gain insights into emerging security threats...Risk Management
Cyber risk management constitutes a multifaceted approach adopted by IT professionals to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities inherent in an organization’s digital infrastructure and operations. Central to this endeavor is the strategic prioritization of cybersecurity initiatives aimed at fortifying the organization’s resilience against evolving cyber threats and minimizing potential risks to...Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation reduces the potential damage an organization will suffer when a breach occurs. While some risks will always be present when operating online, mitigation procedures are intended to reduce any damage that occurs when those risks turn into exploits. Part of a cybersecurity risk mitigation plan might also include communications and marketing procedures to...Risk Prioritization
Security professionals often face many more issues than they can realistically mitigate immediately. They use risk prioritization to determine which risks pose the most serious consequences based on the assets impacted, their connections, exploitability, and other factors.Risk Scoring
Risk scoring is a method security professionals often use to compare and prioritize the severity or exploitability of vulnerabilities. Quantifying the level of risk based on a rating scale provides a more objective way to determine which vulnerabilities to address first. Attack surface management solutions use risk scoring and other methods to prioritize risks and...Risk Tolerance
Businesses always face some level of risk. Risk tolerance is the amount of risk the company is willing to accept. The risk tolerance threshold varies depending on factors such as the assets involved and the value of the data at risk.Rogue Asset
Also known as a malicious asset, a rogue asset is an asset created by a threat actor or an asset stolen by and under the control of a threat actor.S
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
Software-as-a-Service is a software delivery method. Users access SaaS via the internet rather than downloading and installing a software application on a device. SaaS products typically are sold on a subscription basis rather than a one-time purchase.Security Control
Security controls play a crucial role in safeguarding organizational assets and protecting against cybersecurity threats and attacks. By implementing a combination of technical, administrative, and physical controls, organizations can establish a robust security posture that encompasses prevention, detection, and response capabilities. These controls include measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, access controls, encryption, security...Security Monitoring
Security monitoring is the process of continuously scanning a company’s IT systems and maintaining real-time or near-real-time awareness of the activities and events occurring within those systems. Security monitoring solutions alert security teams when abnormal activity is discovered, allowing them to investigate and respond to vulnerabilities and threats before they escalate into an incident that...Security Risk Assessment
The cyber security risk assessment, as delineated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), serves as a fundamental cornerstone in safeguarding organizational operations, assets, and stakeholders against the myriad threats and vulnerabilities pervasive in today’s digital landscape. This comprehensive evaluation encompasses an exhaustive analysis of the risks inherent in the organization’s utilization of...Shadow IT
Shadow IT comprises information technology systems, such as devices, software, services, and applications employees are using without the explicit approval of the company’s IT department. It’s not being actively managed and monitored by the company’s security team, meaning shadow IT can introduce serious security vulnerabilities. Vulnerability scanners only scan what is known — the sources...Social Engineering
Social engineering is a sophisticated cyber attack method that uses manipulation and deception tactics to trick the victim into divulging sensitive information or providing access to information systems containing sensitive data. Social engineering comprises various attack methods such as phishing, ransomware, pretexting, and baiting, among others.Spear Phishing
Spear phishing campaigns pose significant threats to organizations by exploiting human vulnerabilities and leveraging personalization tactics to deceive targets into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that benefit the attacker. Unlike traditional phishing attacks, which cast a wide net to target a broad audience, spear phishing campaigns are highly targeted and tailored to specific individuals...Subsidiary Asset
Subsidiary assets are owned or managed by a company’s subsidiaries outside of the company’s networks. They may be known or unknown. In mergers and acquisitions, subsidiary assets are a prominent concern for parent companies. Attack surface management solutions offering robust digital supply chain discovery identify subsidiary assets, their connections, and any associated risks or vulnerabilities.Supply Chain Risk Management
Digital supply chain risk management is a critical aspect of cybersecurity strategy, particularly in the context of modern business operations that rely heavily on digital technologies and interconnected networks of suppliers, vendors, and service providers. As organizations increasingly embrace digital transformation initiatives and migrate their business processes and applications to online platforms, the complexity and...T
Third-Party Security
As organizations increasingly rely on third-party vendors for critical services and solutions, ensuring robust third-party security measures is paramount. This involves conducting thorough vendor assessments, evaluating their security posture and practices, and establishing clear security requirements in contractual agreements. Moreover, ongoing monitoring and auditing of vendors’ security controls are essential to identify and address potential...Threat Vector
Threat vectors encompass a wide range of techniques and tactics employed by cyber attackers to compromise the security of IT systems and networks. These may include: Exploiting software vulnerabilities Leveraging social engineering tactics such as phishing or pretexting Conducting brute force attacks to guess passwords Exploiting misconfigurations or weaknesses in network infrastructure Using malware such...TPRM: Third-Party Risk Management
Effective TPRM encompasses not only implementing best practices but also maintaining robust oversight and governance mechanisms to ensure the ongoing security of external partnerships. Beyond protecting critical assets and sensitive information, TPRM involves thorough vendor assessments, contractual agreements with clear security requirements, regular monitoring of vendor compliance, and swift remediation of identified risks. By establishing...U
Unknown Asset
An unknown asset is an element that exists within a company’s IT infrastructure without the company’s knowledge. Attack surface management solutions identify unknown assets, such as shadow IT, subsidiary assets, and orphaned apps.V
Vendor-Managed Asset
A vendor-managed asset is an element of a company’s IT infrastructure controlled and managed by a vendor, so the company has no direct control over the asset. These assets may be known or unknown, and they can introduce serious vulnerabilities into the company’s network. Attack surface management solutions provide visibility into vendor-managed assets, how they’re...Vendor Risk Management
Effective vendor risk management is essential for organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate the potential risks associated with third-party relationships and dependencies. Third-party vendors and suppliers play a crucial role in supporting business operations and delivering products and services, but they also introduce inherent risks, including data breaches, compliance violations, and operational disruptions. By implementing...Vulnerability
A vulnerability is a weakness in a company’s systems that provides opportunities for cyber attackers to gain unauthorized access and carry out successful cyber attacks. Vulnerabilities can exist in security policies, security controls, application configurations, code, open ports, and every other area of a company’s information systems.Vulnerability Assessment
Vulnerability assessments play a crucial role in identifying and prioritizing security weaknesses within an organization’s IT infrastructure and applications. By systematically scanning and analyzing systems, networks, and software components for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, vulnerability assessments provide valuable insights into potential security risks and exposures that could be exploited by threat actors. The assessment process...Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management includes processes and solutions to continuously monitor a company’s IT systems, identify potential vulnerabilities, prioritize risks, mitigate risks, and report on incidents.Vulnerability Patching
Vulnerability patching is the process of applying fixes to applications or systems that remediate a discovered vulnerability. They may be implemented as temporary mitigation efforts and incorporated into the next software release, or they may be permanent fixes that eradicate the vulnerability. Regularly checking for updates and installing the most current, secure software versions and...Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is an ongoing process of monitoring a company’s IT networks, systems, and software to identify potential security risks. Vulnerability scanning solutions automate this process and report on abnormal behavior discovered so security teams can take immediate action to remediate or mitigate vulnerabilities.Z
Zero Trust
Zero Trust represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity strategy, challenging traditional notions of trust and security within corporate networks and information systems. Rooted in the principle of pervasive distrust, the Zero Trust model adopts a proactive and holistic approach to security, treating every user, device, application, and network segment as potentially compromised entities, regardless of... - Solutions